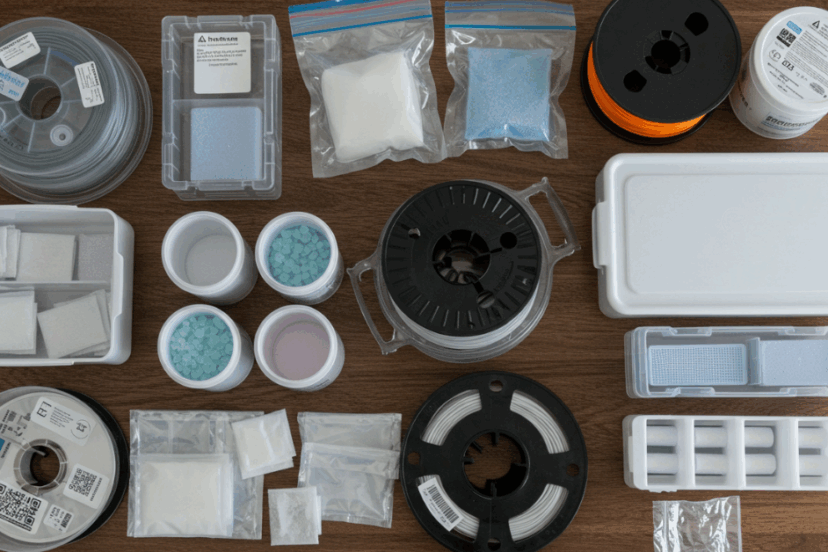
What are other ways to store filament?
There are several ways to store 3D filament to ensure it remains in good condition and ready for use. Each method has its advantages depending on the type of filament and available space. Here are some popular filament storage options:
1. Vacuum-Sealed Bags
- Why It’s Effective: Vacuum-sealed bags remove air, which helps prevent moisture from entering the bag and affecting the filament. These bags can keep your filament dry for extended periods.
- How It Works: Use a vacuum sealer to remove air from the bag and then seal it tightly. You can also add desiccants to further reduce moisture.
- Best For: Moisture-sensitive filaments like Nylon, TPU, and ABS.
2. Dry Box (Filament Dryer Box)
- Why It’s Effective: A dry box helps to keep filament dry by actively controlling the humidity inside the box. Some models come with built-in heating elements to dry the filament as it feeds into the printer.
- How It Works: A dry box uses desiccants and/or a heating element to maintain a dry environment around the filament spools.
- Best For: Filaments that are prone to moisture absorption, especially Nylon, PETG, and ABS.
3. Desiccant Bags or Containers
- Why It’s Effective: Desiccants (such as silica gel) absorb moisture in the air and help prevent filament from getting damp.
- How It Works: Place desiccant packets or silica gel inside airtight containers or plastic bins along with the filament spool. Replace the desiccant as needed when it becomes saturated.
- Best For: Storing filament in bulk or long-term storage for materials like PLA, PETG, and ABS.
4. Plastic Bins with Airtight Seal
- Why It’s Effective: Airtight plastic bins help create a sealed environment that prevents moisture and dust from coming into contact with the filament.
- How It Works: Store filament spools inside an airtight plastic bin, and place desiccants or silica gel inside to absorb any moisture.
- Best For: General storage of PLA, PETG, and other filaments that don’t require active drying.
5. Filament Storage Tubes or Containers
- Why It’s Effective: Specialized filament storage tubes or containers, often with airtight seals, can protect filament from moisture and dust. Some containers are designed with a spool holder to allow easy access to filament while stored.
- How It Works: Simply place the filament spool inside the container, ensuring it’s tightly sealed.
- Best For: Short- to medium-term storage of PLA, ABS, PETG, and other filament types.
6. Spool Holders with Drying Systems
- Why It’s Effective: These systems combine spool holders with built-in drying mechanisms (such as a desiccant compartment or heating element) that continuously dry the filament as it’s used.
- How It Works: These storage units provide both moisture protection and a controlled environment while you’re actively using the filament in your 3D printer.
- Best For: Nylon, TPU, and filaments that require a consistent dry environment during use.
7. Filament Drying Ovens
- Why It’s Effective: Filament drying ovens are designed to remove moisture from filament before it’s used in a print. Some models offer adjustable temperature controls to avoid overheating the filament.
- How It Works: Place your filament spools in the drying oven at a low temperature (usually between 40°C to 50°C) for several hours to remove moisture.
- Best For: Nylon, TPU, ABS, and any filament that has absorbed moisture.
8. Vacuum-Sealed Boxes or Containers
- Why It’s Effective: Similar to vacuum-sealed bags, vacuum-sealed boxes can keep filament dry by creating an airtight environment, reducing moisture exposure.
- How It Works: Use a vacuum pump to evacuate air from the box and seal it tightly. You can include desiccants inside for added moisture control.
- Best For: High-humidity environments or filaments that require extra moisture protection, such as Nylon and TPU.
9. Use of Humidity-Controlled Cabinets
- Why It’s Effective: Humidity-controlled cabinets provide a consistent environment where the humidity levels are maintained at an optimal range, which is ideal for filament storage.
- How It Works: The cabinet contains built-in controls for regulating humidity, and some models even feature heating elements to maintain a dry environment.
- Best For: High-value or moisture-sensitive filaments like Nylon and TPU, or for those who live in areas with high ambient humidity.
10. Filament Storage on Spool Hangers
- Why It’s Effective: Spool hangers help to store filament spools off the floor, preventing the filament from gathering dust or moisture from the ground. You can place these spools in plastic bags or storage bins for added protection.
- How It Works: Hang the filament spool from a hook or stand, and store it in a clean, dry area. You can place desiccants or moisture absorbers nearby for additional protection.
- Best For: Storing filament that’s actively being used, such as PLA, PETG, and ABS.
Summary of Storage Methods:
- Vacuum-Sealed Bags: Best for moisture-sensitive filaments like Nylon and TPU.
- Dry Box: Great for Nylon and other filaments prone to moisture absorption.
- Desiccant Bags or Containers: A simple and effective way to store filament in bulk.
- Plastic Bins with Airtight Seal: Ideal for general storage of most filaments.
- Filament Storage Tubes: Convenient for short- to medium-term storage.
- Spool Holders with Drying Systems: Keeps filament dry during active use.
- Filament Drying Ovens: Removes moisture from filament before use, especially for Nylon and TPU.
- Vacuum-Sealed Boxes: Provide extra protection by creating an airtight environment.
- Humidity-Controlled Cabinets: Perfect for consistent humidity control and long-term filament preservation.
Choosing the right filament storage method depends on factors like filament type, available space, and how long the filament will be stored. For optimal results, ensure you use airtight containers, desiccants, or drying systems to protect your filament from moisture and environmental factors.