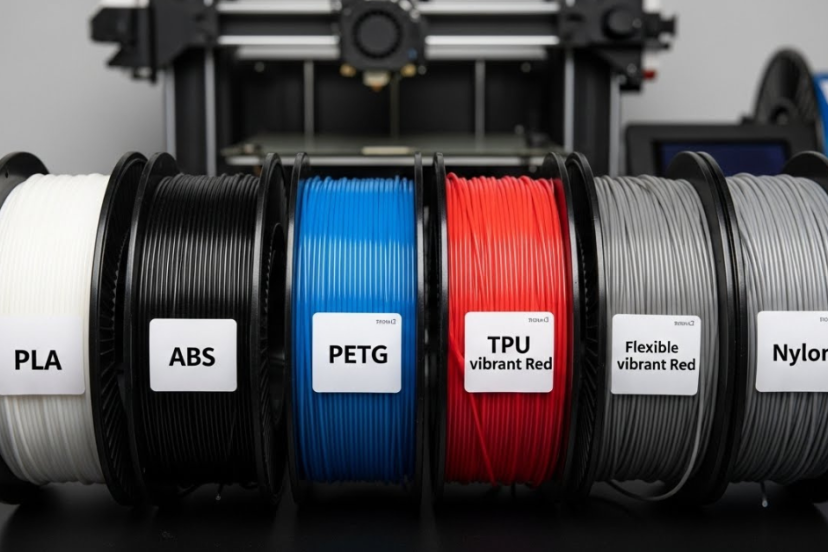
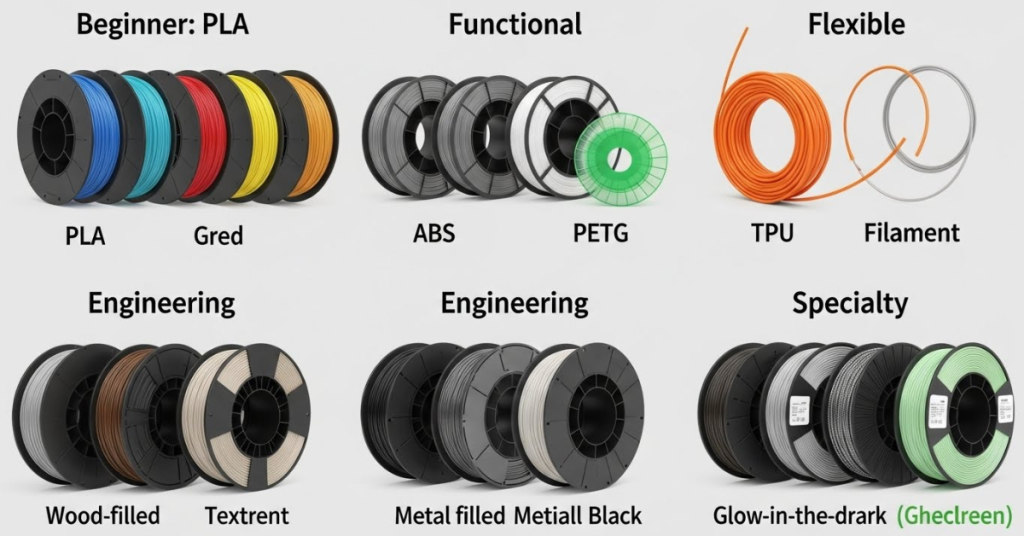
Filament Types
When it comes to 3D printing, the filament you choose plays a crucial role in determining the quality, durability, and functionality of your prints. With a wide range of filament options available, it’s important to understand the characteristics and benefits of each type. In this article, we will explore various filament types commonly used in 3D printing and provide insights into their properties, applications, and recommendations.
Importance of Choosing the Right Filament
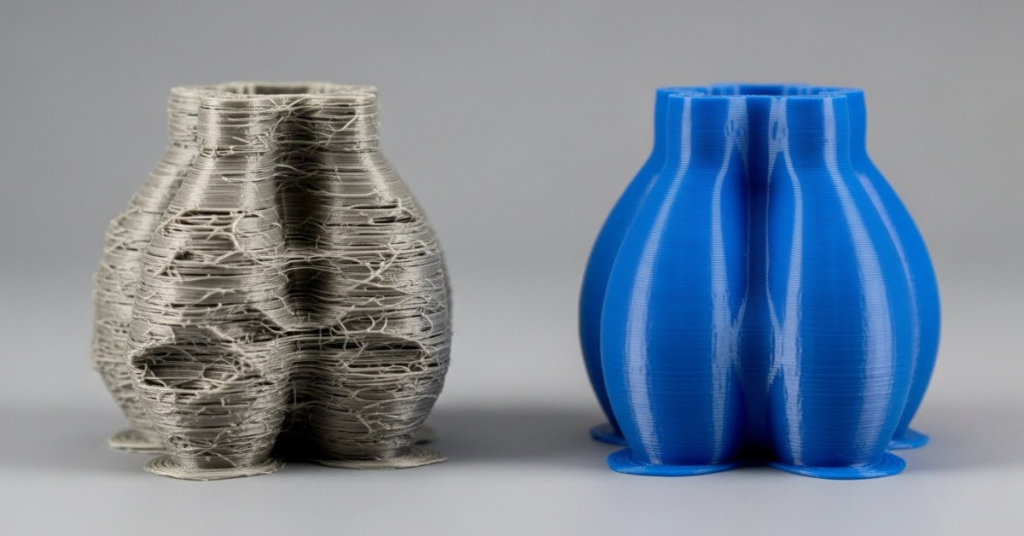

Selecting the appropriate filament is essential to achieve the desired results in your 3D prints. Each filament type has its own unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications. By understanding the strengths and limitations of different filaments, you can make informed decisions and optimize your 3D printing projects.
PLA: Biodegradable and Beginner-Friendly Filament
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is one of the most popular and widely used filaments in 3D printing. It is derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, making it an environmentally friendly choice. PLA is known for its ease of use, making it ideal for beginners and educational settings.
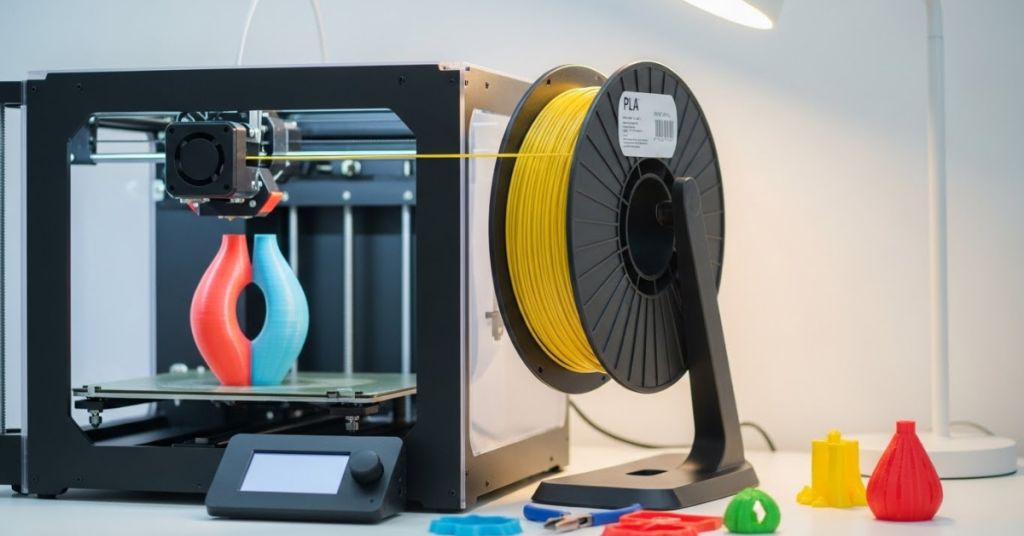

Advantages of PLA:
Biodegradable: PLA is biodegradable, which means it can naturally break down over time, reducing its environmental impact.
Easy to Print: PLA requires lower printing temperatures compared to other filaments, resulting in less warping and clogging issues.
Wide Color Options: PLA filaments are available in a vast array of colors, allowing for creative and vibrant prints.
Low Odor: PLA emits a mild, sweet smell during printing, making it more pleasant to work with compared to some other filaments.
Best Use Cases for PLA:
PLA is well-suited for a range of applications, including:
Prototyping: PLA’s ease of use and accuracy make it a popular choice for rapid prototyping and functional testing.
Educational Settings: Its beginner-friendly nature, safety, and eco-friendliness make PLA ideal for educational environments.
Decorative Prints: PLA’s wide color options and smooth finish make it great for creating decorative or artistic objects.
ABS: Durable and Heat-Resistant Filament for Functional Prints
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a strong and durable filament widely used for functional prints. It offers excellent mechanical properties and higher temperature resistance compared to PLA, making it suitable for engineering applications.
Advantages of ABS:
Strength and Durability: ABS prints are known for their toughness and ability to withstand impacts, making them suitable for functional parts.
Heat Resistance: ABS has a higher glass transition temperature than PLA, allowing it to withstand higher temperatures without deforming.
Post-Processing Options: ABS can be easily sanded, glued, and painted, offering versatility in post-processing and finishing.
Best Use Cases for ABS:
ABS is commonly used in the following applications:
Functional Parts: Its strength and durability make ABS a preferred choice for manufacturing functional components, such as automotive parts or tools.
Enclosures and Prototypes: ABS’s temperature resistance and post-processing options make it suitable for creating enclosures and prototypes that require finishing touches.
Engineering Applications: ABS’s mechanical properties and ability to withstand high temperatures make it suitable for engineering applications that require robustness and durability.
PETG: Strong and Flexible Filament with Good Chemical Resistance
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified) is a popular filament known for its balance between strength, flexibility, and ease of use. It combines the best characteristics of PLA and ABS, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Advantages of PETG:
Strength and Flexibility: PETG exhibits higher impact resistance and flexibility compared to PLA and ABS, making it suitable for functional parts that require some degree of flexibility.
Chemical Resistance: PETG is more resistant to chemicals and solvents than PLA or ABS, making it suitable for applications where exposure to such substances is expected.
Transparency: PETG is available in transparent variants, allowing for the creation of see-through or light-transmitting prints.
Best Use Cases for PETG:
PETG finds applications in various fields, including:
Functional Prototypes: PETG’s combination of strength and flexibility makes it an excellent choice for prototyping functional parts with moderate load requirements.
Outdoor Applications: PETG’s resistance to UV radiation and moisture makes it suitable for outdoor use, such as signage or garden tools.
Containers and Packaging: PETG’s chemical resistance and transparency make it a preferred choice for creating containers and packaging materials.

TPU: Flexible Filament Ideal for Creating Rubber-Like Objects
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a highly flexible filament that allows for the creation of rubber-like objects. It exhibits excellent elasticity, impact resistance, and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for various applications requiring flexibility.
Advantages of TPU:
Flexibility and Elasticity: TPU can be stretched and bent repeatedly without losing its original shape, making it ideal for producing flexible parts or prototypes.
Impact Resistance: TPU has excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for applications that require shock absorption or vibration dampening.
Versatility: TPU can be used to create a wide range of objects, from shoe soles to protective cases.
Best Use Cases for TPU:
TPU finds applications in numerous industries, including:
Wearables: TPU’s flexibility and comfort make it an excellent choice for creating wearables such as smartwatch bands or athletic equipment.
Gaskets and Seals: TPU’s excellent elasticity and resistance to various substances make it ideal for producing gaskets, seals, or O-rings.
Grips and Handles: TPU’s non-slip properties and durability make it suitable for creating ergonomic grips and handles.
Nylon: Tough and Versatile Filament for Engineering Applications
Nylon filaments are known for their strength, toughness, and versatility. They offer excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and low friction, making them suitable for demanding engineering applications.
Advantages of Nylon:
Strength and Durability: Nylon is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for load-bearing applications that require toughness and durability.
Chemical Resistance: Nylon exhibits excellent resistance to various chemicals, oils, and solvents, making it suitable for applications that involve exposure to such substances.
Low Friction: Nylon has low friction properties, making it suitable for moving parts, gears, or bearings.
Best Use Cases for Nylon:
Nylon is commonly used in the following applications:
Functional Prototypes: Nylon’s strength and durability make it ideal for prototyping functional parts that require high mechanical performance.
Manufacturing Tools: Nylon can be used to create custom jigs, fixtures, or tooling due to its toughness and resistance to wear.
Engineering Components: Nylon is often used to manufacture gears, bushings, or bearings due to its low friction and self-lubricating properties.

Specialized Filaments: Wood, Metal, Carbon Fiber, and More
In addition to the standard filaments mentioned above, there is a wide range of specialized filaments available that can add unique properties to your prints. These filaments are often infused with wood fibers, metal particles, carbon fiber, or other additives to provide distinct characteristics.
Advantages of Specialized Filaments:
Enhanced Aesthetics: Specialized filaments can add a realistic wood-like appearance, metallic finishes, or carbon fiber textures to your prints.
Improved Strength and Rigidity: Filaments infused with additives such as carbon fiber or metal particles can significantly enhance the strength and rigidity of printed objects.
Customization: Specialized filaments offer opportunities for creative expression and customization by adding unique textures, colors, or finishes to your prints.

Best Use Cases for Specialized Filaments:
Specialized filaments find applications in various creative and functional areas, such as:
Artistic and Decorative Prints: Wood-infused filaments can add a natural wood appearance to sculptures, artistic objects, or home decor items.
Functional Prototypes: Filaments infused with metal particles or carbon fiber can be used to create functional prototypes that require enhanced strength or heat resistance.
Engineering Applications: Specialized filaments can be utilized in engineering applications where specific properties like electrical conductivity, thermal resistance, or high stiffness are required.
Considerations When Choosing Filaments
When selecting the right filament for your 3D printing project, there are a few factors to consider:
Printer Compatibility: Ensure that the filament you choose is compatible with your 3D printer’s specifications, including nozzle temperature and diameter requirements.
Project Requirements: Consider the specific properties required for your print, such as strength, flexibility, temperature resistance, or chemical resistance.
Environmental Impact: If sustainability is a concern, opt for biodegradable filaments like PLA to reduce your ecological footprint.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and achieve optimal results with your 3D prints.
Conclusion

Choosing the right filament is crucial for successful 3D printing projects. Each filament type, from beginner-friendly PLA to specialized filaments like wood or metal-infused, offers unique properties and advantages. Understanding the strengths, limitations, and best use cases for each filament allows you to optimize your prints for specific applications. Consider your project requirements, printer compatibility, and environmental impact when making filament choices, ensuring that your 3D prints meet your expectations.
FAQs

- Can I use PLA for functional parts?
While PLA is not as strong as some other filaments, it can be suitable for certain low-stress functional parts. However, for applications that require higher strength, durability, or temperature resistance, consider other filaments like ABS or Nylon. - Are specialized filaments more expensive than standard filaments?
Yes, specialized filaments tend to be more expensive due to the additional materials and manufacturing processes involved. However, the added properties and unique aesthetics they offer can justify the cost for specific projects. - Can I mix different filaments in a single print?
While it’s technically possible to mix filaments in a single print, it requires advanced techniques and may not always yield desired results. It’s generally recommended to use one type of filament per print to ensure consistent quality. - How do I store filament to prevent moisture absorption?
Filaments like PLA and ABS can absorb moisture from the air, which can negatively impact print quality. To prevent this, store your filaments in airtight containers with desiccant packs or invest in filament dryers for long-term storage. - Are there any safety precautions I should take when 3D printing with filaments?
Yes, it’s important to follow safety guidelines when 3D printing, including proper ventilation in the printing area and avoiding inhalation of fumes. Each filament may have specific safety considerations, so refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for handling and printing.